 Power
Plants
Power
PlantsFunctions of the
Electric Generators
Electric generators are a necessity in today's world. They come in all shapes and sizes, allowing them to meet the power needs of our modern world. Listed below are four examples of generators that are commonly found in our everyday life.
 Power
Plants
Power
Plants
Power Plants are the most recognizable location where someone can find generators operating on a regular basis. Basic power plants use steam to drive turbines which spin the generators. This steam is made by burning fossil fuels, which in turn heat liquid water to produce the steam. Other common types of power plants include nuclear plants and hydroelectric plants. Nuclear plants harness the heat produced in fission to spin the generators while hydroelectric plants use rushing water to spin turbines which spin the generators. In all these cases, turbines are all used to spin the generators because of there simplicity of operation and there high reliability.
 Portable
Generators
Portable
Generators
Portable generators are essentially miniaturized versions of a power plant. The major difference between ordinary power plants and portable generators is in the method used to spin the generator. In the small generators, a reciprocating internal combustion engine is used over a turbine engine. Manufactures prefer reciprocating engines for these devices because they are smaller and use readily available fuels such as gasoline or diesel. These devices are often used at construction sites that do not have easy access to electricity, tailgating football fans across the country, and campers who can't do without certain electronic devices.
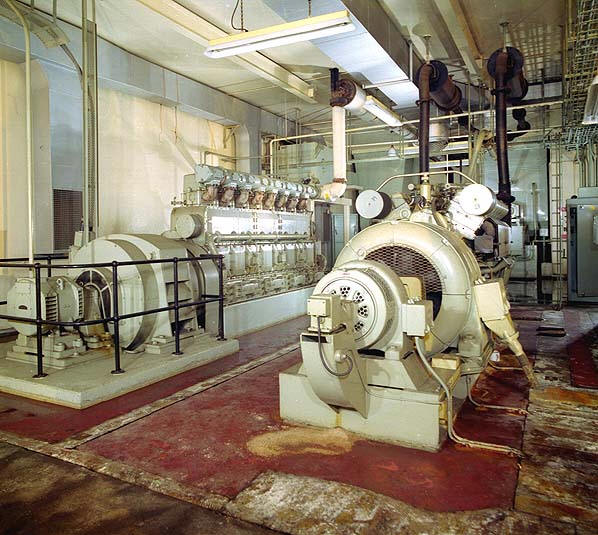
Stand-By Generators
Stand-By generators fall in between larger power plants and smaller portable generators. Like their smaller brethren, the portable generator, stand-by generators use reciprocating internal combustion engines to keep the generator spinning. Since these devices are much larger and are expected to produce much more power, they tend to use diesel engines which are more efficient and reliable than gasoline engines. These generators are used in facilities that must have electricity at all time. Stand-By generators are common place at hospitals and facilities operated by high-tech industry related businesses.

Diesel-Electric Trains
Diesel electric trains are like mini power plants tucked into a locomotive. These trains use massive diesel driven generators to produce the electricity necessary for the electric motors that drive the trains. These trains were and upgrade over the old steam engines because they produce less pollution, pull more goods, faster, and easier to operate. They use the hybrid diesel electric technology because of the power band characteristics of electric motors. These motors always produce the same amount of torque all the time, which makes them ideal for pulling at slow speeds. They also eliminate the need for a transmission, which saves space and eliminates one more mechanical item that can break.